The Freeze Drying (or Lyophilisation) procedure is a kind of very highly developed and proven technique in lyophilisation service providers in the Food, Pharmaceutical, Nutraceutical and Biotech Industries. It is an ideal solution for large corporations that sell food products worldwide, due to the ability to easily ship frozen, dehydrated products. Consumers are increasingly demanding fresh, superior-quality products with a longer shelf life, making this an extremely valuable technology for manufacturers. There is a growing demand for Freeze Dried technology and Freeze Dried products to create Speciality Meals, Medications and Freeze Dried Fruits and Vegetables.
This blog will explore the complete freeze-drying process in detail, as well as the advantages of utilising drying technology in today’s market and how freeze-drying technology is rapidly becoming the most prominent method for manufacturing freeze-dried goods around the world.
Want to optimise your Food Business? Request a free consultation!
Food Product Development Services – Click Here
Understanding Freeze Drying Technology& Formulation 
Lyophilisation, or freeze drying, is a dehydration process that removes water from products without exposing them to damaging heat.
The process happens in controlled stages:
1. Freezing Stage
The product is first frozen at extremely low temperatures to stabilise its structure and preserve sensitive components.
2. Primary Drying (Sublimation)
The pressure is reduced inside the chamber, causing frozen water to convert directly from ice to vapour without becoming liquid. This stage removes most of the moisture.
3. Secondary Drying
The final stage removes residual moisture to ensure long-term product stability. This method allows freeze-dried food and other sensitive materials to retain their structure, flavour, nutrients, and bioactive compounds.
Proper drying formulation is also essential to maintain consistent drying rates, avoid product collapse, and ensure reliable commercial production.
You May Also Like: Food Packaging and Labelling
How Freeze Drying Differs from Conventional Drying Methods
| Aspects | Traditional Drying Method | Freeze Drying |
| Drying method | Uses heat to evaporate moisture | Removes moisture through sublimation without heat |
| Effect on product texture | Texture is often altered or collapsed | Original structure preserved on a large scale |
| Flavour / aroma | Partial loss due to heat exposure | Natural flavour and aroma retained |
| Nutritional value | Heat-sensitive nutrients may degrade | High retention of nutrients and bioactives |
| Rehydration | Slow and incomplete | Fast and nearly complete rehydration |
| Shelf life | Moderate, often needs preservatives | Long shelf life without preservatives |
| Commercial focus | Speed and cost efficiency | Quality, stability, and premium value |
| Best suited for | Mass-produced, low-cost products | Higher value, sensitive products |
Key Benefits of Freeze-Dried Products 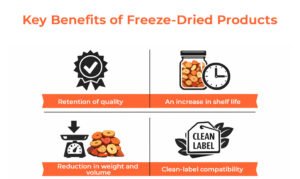
1. Retention of quality:
One of the main advantages of freeze-drying is the ability to preserve the natural colour, flavour, texture, and nutritional value of products.
Heat-sensitive ingredients such as vitamins, enzymes, and bioactive compounds remain largely intact.
2. An increase in shelf life:
Because almost all moisture is removed, microbial growth and enzyme activity are significantly reduced. This allows freeze-dried foods to remain stable for extended periods when packaged properly.
This makes the technology ideal for global food distribution and export markets.
3. Reduction in weight and volume:
Removing moisture drastically reduces product weight and volume. As a result, freeze-drying products are easier and more economical to transport and store.
This advantage is particularly valuable for:
- Military and emergency nutrition supplies
- Export-focused food brands
- Space-efficient food logistics
4. Clean-label compatibility:
It eliminates the need for chemical preservatives. This allows brands to produce clean-label freeze-dried food products that align with modern consumer preferences.
Role of Freeze Drying in the Food Industry
The food industry is one of the largest users of freeze drying technology.
Common freeze-dried foods include:
- Fruits and vegetables
- Herbs and spices
- Instant coffee
- Dairy ingredients
- Ready-to-eat meals
- Nutritional powders
Freeze drying preserves taste, colour, and structure while enabling fast rehydration, making products more appealing than traditionally dried alternatives.
It also supports the development of foods containing:
- Heat-sensitive nutrients
- Natural colours
- Functional ingredients
This makes drying particularly valuable in premium snacking, health foods, and export-oriented food products.
Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Applications
Beyond food, Lyophilisation plays a critical role in the pharmaceutical and biotech industries.
Many pharmaceutical products such as:
- Vaccines
- Biologics
- Injectable drugs
are highly sensitive to heat and moisture.
It helps extend their shelf life and allows storage at room temperature, reducing dependence on complex cold-chain logistics.
Biotechnology companies also rely on freeze drying to preserve:
- Enzymes
- Probiotic cultures
- Diagnostic reagents
- Biological samples
This ensures the materials maintain their biological activity and functional performance.
Industrial and Speciality Uses
It is also used in several specialised industries.
Examples include:
- Cosmetic companies preserving botanical extracts
- Pet food manufacturers producing premium raw-style products
- Research laboratories preserving biological samples
In these sectors, product stability and functionality are more important than processing cost, making drying the preferred preservation technique.
Freeze Drying Equipment and Process Control
Modern drying systems are highly automated and consist of several integrated components:
- Freeze dryer chamber
- Vacuum system
- Condenser
- Heated shelves
- PLC automation systems
These systems are available in different scales, from pilot-scale R&D equipment to large industrial production units.
One major advantage is the ability to scale from product development to commercial manufacturing without redesigning the entire process.
Challenges and Operational Considerations
Despite its benefits, it also presents some challenges.
- High Initial Investment: Freeze drying equipment requires significant capital investment.
- Energy Consumption: The process is time-intensive and requires high energy input.
However, modern technologies, improved system design, and process optimisation are helping reduce these limitations.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
Global trends such as increased demand for nutraceutical and functional foods, growth of biologics and vaccines, consumer demand for clean-label products, and demand for products with longer shelf lives have all contributed positively to the growth of freeze drying. In particular, the demand for freeze-drying technology is growing in emerging markets, with the opportunity to produce high-value products and, in turn, provide better quality customer service.
Trending Right Now: High-Protein Snacks Development
Conclusion
Freeze drying (Lyophilisation) is a powerful preservation technology that helps maintain the quality, nutrition, and shelf life of sensitive products. From freeze-dried foods to pharmaceutical products, this process enables manufacturers to create stable, lightweight, and high-value products.
Looking to develop freeze-drying products?
Connect with Foodsure for expert guidance in product development and scalable manufacturing.
Need Expert Help to Launch Your Food Product Legally & Successfully?
Foodsure supports food brands with FSSAI-compliant labelling, pre-launch checks, and regulatory compliance to ensure a smooth and legal food product launch. We help prevent penalties and delays before your product enters the market.
What We Help You Solve
-
FSSAI label review and correction
-
Nutritional panel accuracy and ingredient validation
-
Claim verification and compliance
-
Packaging artwork and readability checks
-
Audit, inspection, and documentation support
Who We Work With
-
Startups launching new food products
-
FMCG and D2C food brands
-
Private label and co-manufacturers
-
Importers, exporters, and suppliers
Frequently Asked Questions
What is freeze drying formulation?
It refers to designing ingredient compositions that remain stable, functional, and high quality during freeze drying and after rehydration.
Why is formulation important in freeze drying?
Proper formulation prevents structural collapse, poor rehydration, moisture retention, and loss of flavour or bioactive properties.
Which industries use freeze drying formulation the most?
Food, nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, biotech, and ingredient manufacturing industries widely use drying formulations for sensitive products.
Can all ingredients be freeze dried?
Not all ingredients perform well without formulation adjustment. Some require carriers or stabilisers to maintain structure and stability.
How does formulation affect shelf life?
Optimised formulations reduce residual moisture, improve stability, and significantly extend shelf life without chemical preservatives.
What role do carriers play in freeze drying?
Carriers improve drying efficiency, prevent stickiness, and enhance powder flow and rehydration performance.
Is freeze drying formulation scalable?
Yes. When developed correctly at pilot stage, freeze drying formulations can be scaled reliably to commercial production.