Food is never simply food. Everything has its purpose, and each element will respond uniquely within a system. The texture, flavour, and shelf life are defined by carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Nutrition, stability, and nutritional positioning are determined by vitamins, minerals, and additives. Even cooking, fermenting or preserving the product can change the final product radically.
Understanding these interactions across different types of food turns food product development into a structured strategy rather than intuition.
This blog describes why a food consultant will profile and judge food at each stage, to make it taste good, stable and successful in the marketplace.
Classification of the Different Types of Food
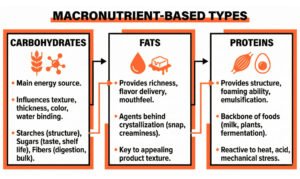
1. Macronutrient-Based Types
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the ultimate source of energy in the body, though in product development, they play a much greater role. These affect thickness, structure, colour, sweetness and moisture retention. Many products have their structure based on starches. Sugars add flavour as well as affect the browning and shelf life. The fibres alter the texture, enhance bulk and digestive capability. Carbohydrates create the framework behind the experience in food systems.
Fats
Fats are what make the foods rich; they bring the flavour compounds to the fore, and they decide the texture of the food in the mouth. Besides, they are the main agents behind crystallisation, which in turn influences the snap of chocolate or the creaminess of spreads. The correct selection of fat is usually what separates a product that charms from a product that simply feels banal.
Proteins
Proteins provide structure, foaming ability, and emulsification power. In fact, proteins from milk, plants, or fermentation serve as the backbone of almost everything from baked goods to beverages. Their reaction to heat, acid, or mechanical stress is what makes them one of the most challenging technical ingredients to handle.
2. Micro-Ingredient Categories
Vitamins
Vitamins are the elements that define the nutritional profile; however, the main issue is their stability. They are destroyed by light, heat, and oxygen; therefore, the formulation should be done in a way that allows the vitamins to be partially exposed to these factors while still delivering the intended health claims.
Minerals
From a nutritional point of view, minerals are very simple, but they can change pH, interact with proteins, and alter flavour. These are small ingredients that have a surprisingly big influence.
You May Also Like: Trends in Food Product Development
3. Processing-Level Classification
Raw Foods
Raw materials are the things that determine the baseline for everything. Their variability, moisture, and natural enzyme activity are the factors that define how the final product will be predictable.
Cooked & Heat-Treated Foods
By heat, flavours are released, the product becomes safer, and the structure changes. The main thing is to control the reactions in such a way that the result is consistent from batch to batch.
Preserved Foods
Whether it is drying, fermenting, pickling, or using preservatives, the common goal of all these methods is stability. Each method alters the texture and flavour differently; therefore, the choice determines not only the properties of the final product but also its whole identity.
Want to optimise your Food Business? Request a free consultation!
Explore Our Exclusive Food Product Development
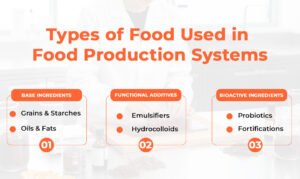
Types of Food Used in Food Production Systems
Base Ingredients
- Grains & Starches: They confer body, structure and thickening qualities to different food systems.
- Oils & Fats: Beyond nutrition, fats act as lubricants, texture modifiers, and flavour carriers. Their melting point profiles matter more than most people realise.
Functional Additives
- Emulsifiers: When water and oil refuse to cooperate, emulsifiers step in. They hold systems together, stabilise foams, and prevent separation.
- Hydrocolloids: These gums and gels control water like nothing else. They set textures from fluid to firm and keep products stable during storage.
Bioactive Ingredients
- Probiotics: Live cultures add both health benefits and processing challenges. They demand careful temperature control and packaging choices.
- Fortifications: Iron, omega-3s, vitamins, and other nutrients elevate the product’s value, but they can introduce off-flavours or instability if not balanced correctly.
You May Also Like: Food Packaging and Labelling Regulations
Scientific Approach to Product Development
Technical Feasibility
- Ingredient Interactions: Ingredients do not often act separately. Proteins bind minerals. Fats affect the release of flavours. Starches are sensitive to moisture and heat.
- Stability Assessment: A product might look perfect on day one, then fall apart by week three. Predicting oxidation, moisture migration, and texture drift is essential.
Sensory Profiling & Optimisation
- Texture Sensory Tools: Texture defines a product as much as flavour. Tools like rheology curves or bite-force tests help quantify what the tongue already knows.
- Flavour Sensory Mapping: Flavour isn’t just taste; it’s aroma, mouthfeel, and after-notes. Mapping these elements helps refine a product until it hits the right balance.
Shelf-Life & Packaging Studies
- Chemical Stability: Oxidation, pH shifts, and nutrient degradation all shape shelf life. Good packaging slows these down.
- Microbial Stability: Safety validation is a way of adhering to compliance, and it safeguards brand credibility.
You May Also Like: Art and Science of Food Production
Create Your Signature Food Product Today!
From recipe to launch, our experts turn your Food idea into a market-winning product.
⭐ Rated 4.9/5 by 100+ D2C Founders & FMCG Brands
How Foodsure’s Food Consultants Evaluate Food Categories
Market & Consumer Insights
- Category Trends: Trends show where demand is heading, but knowing which ones will last requires real data, not guesses.
- Benchmarking: Comparing products side by side exposes gaps, strengths, and opportunities. It’s the fastest way to understand a category’s expectations.
Supply Chain & Manufacturing Feasibility
- Cost Analysis: Great ideas still have to make financial sense. Cost modelling keeps ambition grounded in reality.
- Ingredient Availability: If an ingredient is rare or unstable, it can strain production. Feasibility starts with supply consistency.
Commercial Positioning
- Claims & Marketing: Nutrition claims, processing claims, and sustainability claims all need evidence and regulatory alignment.
- Regulatory Compliance: What this really means is that every decision must hold up under scrutiny. Compliance guides the entire development path.
Emerging Types of Foods Shaping the IndustryPlant-Based Proteins
Meat Alternatives: These rely on structure-building proteins, fat systems, and flavour design to closely resemble the familiar without losing their own unique character.
Dairy Alternatives: The main difficulty is that the product has to be simultaneously creamy, high in protein, and heat-stable, in particular, if it is to be used for melting or foaming.
Precision Fermentation Foods
Novel Proteins: Such products provide a level of purity and consistency that farming is not always able to deliver. Moreover, they serve as a stepping stone for the creation of novel product categories.
Enzyme-Based Solutions: By means of enzymes, the texture can be changed, sugars can be decreased, or flavour pathways can be accessed; in most cases, the label remains unchanged.
Sustainable Food Systems
Upcycled Foods: Utilising byproducts is definitely a green practice; however, it very often can bring unique functional properties that you won’t be able to get in any other way.
Regenerative Agriculture Outputs: Elements that come from regenerative situations are not only more earth-friendly, but in a majority of cases, they also possess higher nutrient density.
You May Also Like: Food Business Ideas
Foodsure’s Perspective on the Future of Food Categories
Learning about the types of foods is beyond the identification of ingredients. It involves studying the reaction of components, processing changes in components and how stability influences the performance. Product development is scientifically evaluated, and it becomes organised, scalable, and business-oriented. Food is a system, and the secret of success in it is to know how the system functions.
Let’s bring your food idea to life and turn it into a market-winning product with the best Food Production Company in India.
Book a FREE call with our formulation expert. Contact now at +91 8130404757
“Read More Blogs Related to Food Product Development”
👉 10 Stages of Food Product Development
👉 Leading Food Testing Laboratory in India
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the main types of food?
The main types of food are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water, each serving a unique role in nutrition.
Q2. What are processed foods?
Processed foods are foods that have been altered from their natural state, often for convenience, preservation, or flavour, like canned vegetables, chips, and ready-to-eat meals.
Q3. What is the difference between plant-based and animal-based foods?
Plant-based foods come from plants (fruits, vegetables, grains), while animal-based foods come from animals (meat, fish, eggs, dairy).
Q4. Why is it important to eat a variety of foods?
Eating a variety of foods ensures you get all essential nutrients, supports overall health, and reduces the risk of nutrient deficiencies.
Q5. What are examples of high-protein foods?
High-protein foods include chicken, fish, eggs, beans, lentils, tofu, and nuts. Protein is essential for muscle growth and repair.
Q6. What are examples of high-carbohydrate foods?
High-carbohydrate foods include rice, pasta, bread, potatoes, and cereals, which provide energy for daily activities.
Q7. What foods should be eaten in moderation?
Foods high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats, such as sugary drinks, fried snacks, and processed meats, should be eaten in moderation.